How a Healthy Gut Supports Digestion and Overall Wellness
Gut Microbiome and Digestive Balance
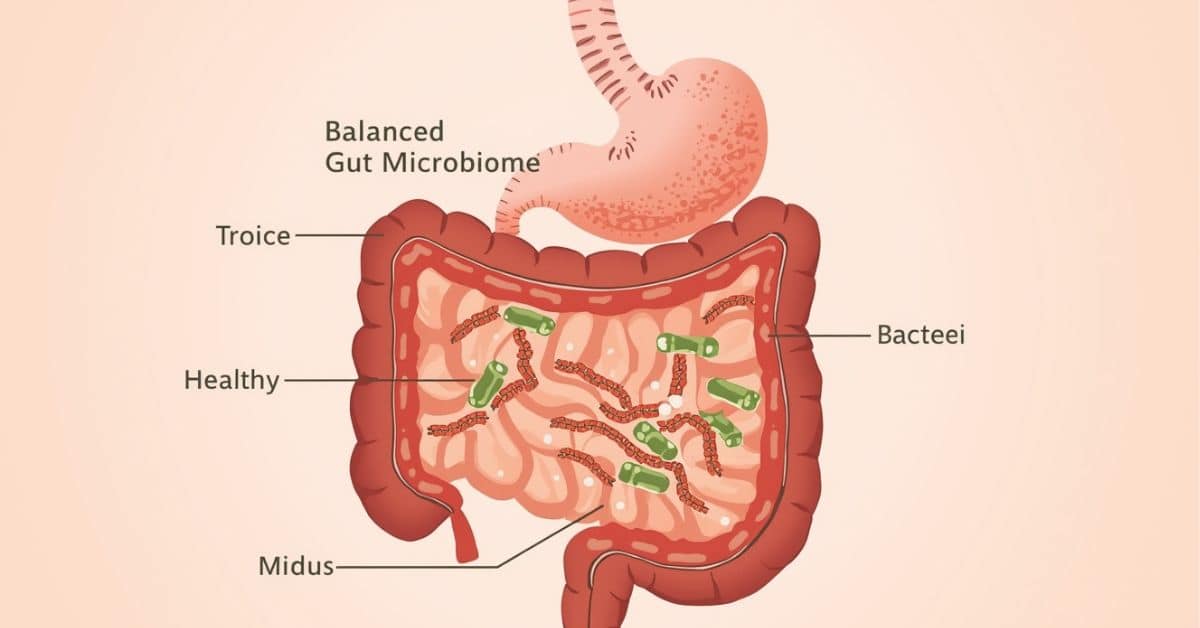
Gut microbiome and digestive balance are closely connected and play a crucial role in how the body processes food, absorbs nutrients, and maintains internal stability. The gut microbiome refers to the trillions of microorganisms living inside the digestive tract, including beneficial bacteria that support digestion and gut function.
When this microbial ecosystem remains balanced, digestion becomes more efficient and comfortable. When disrupted, digestive discomfort and imbalance may occur.
What Is the Gut Microbiome?
Gut Microbiome and Digestive Balance
The gut microbiome is a complex community of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that live primarily in the intestines. These microorganisms help break down food, produce essential compounds, and interact with the digestive system in important ways.
A diverse and balanced gut microbiome supports smoother digestion, while a lack of balance may interfere with how the body handles certain foods.
Gut Microbiome and Digestive Balance Explained
Gut microbiome and digestive balance depend on how well beneficial bacteria coexist with other microorganisms in the digestive system. Beneficial bacteria assist in breaking down fiber, supporting nutrient absorption, and maintaining gut lining integrity.
When harmful bacteria dominate, digestion may become less efficient, leading to discomfort, bloating, or irregular digestion patterns.
Signs of Digestive Imbalance
Digestive imbalance may present itself through several common signs, including:
- Occasional bloating
- Digestive discomfort after meals
- Irregular bowel habits
- Sensitivity to certain foods
These signs may indicate that the gut microbiome is not functioning optimally.
How Diet Influences Digestive Balance
Gut Microbiome and Digestive Balance
Diet plays a major role in shaping the gut microbiome. Diets rich in fiber and whole foods help nourish beneficial bacteria, while diets high in refined sugars and ultra-processed foods may disrupt microbial balance.
Foods that commonly support digestive balance include:
- Fiber-rich vegetables
- Whole grains
- Fermented foods
- Hydrating foods
Consistent dietary choices help maintain a stable digestive environment over time.
Lifestyle Factors That Affect Digestion
Gut Microbiome and Digestive Balance
Beyond diet, lifestyle habits strongly influence gut microbiome and digestive balance. Stress, poor sleep, dehydration, and lack of physical activity can all impact how the digestive system functions.
Simple habits such as staying hydrated, managing stress levels, and maintaining a regular routine help support gut stability and digestive comfort.
Supporting Digestive Balance Long-Term
Gut Microbiome and Digestive Balance
Rather than focusing on quick fixes, long-term digestive balance is best supported through consistent habits. Supporting beneficial gut bacteria helps create a digestive environment that adapts more easily to daily challenges.
Educational approaches emphasize understanding digestion as a gradual process that benefits from balance, patience, and sustainable lifestyle choices.
In addition to digestion, a balanced gut microbiome supports overall digestive resilience. When beneficial bacteria are present in adequate diversity, the digestive system becomes more adaptable to daily dietary changes and environmental factors. This adaptability helps the body respond better to occasional dietary challenges without significant discomfort.
Maintaining digestive balance also supports the integrity of the gut lining. A healthy gut environment helps protect the intestinal barrier, which plays an important role in nutrient absorption and digestive comfort. When the gut lining remains strong, digestion becomes more efficient and the body is better equipped to process essential nutrients from food.
Another important aspect of digestive balance is consistency. The gut microbiome responds positively to regular routines, including consistent meal timing, hydration, and sleep patterns. These habits support stable digestive rhythms and contribute to long-term gut comfort.
Educational approaches to gut health emphasize understanding digestion as a dynamic and evolving process. Supporting the gut microbiome is not about achieving perfection, but about maintaining balance over time. Gradual improvements in dietary choices and daily habits can have a meaningful impact on digestive wellness.
Conclusion
Gut microbiome and digestive balance are fundamental to overall digestive wellness. A balanced microbial environment supports efficient digestion, nutrient absorption, and digestive comfort throughout daily life. When gut bacteria remain in harmony, the digestive system functions more smoothly and adapts better to routine challenges.
By focusing on long-term habits such as balanced nutrition, hydration, stress management, and routine consistency, supporting digestive balance becomes more achievable and sustainable. Rather than relying on short-term approaches, prioritizing gut health helps create a stable foundation for digestive comfort and overall well-being.